Environment
- Basic Environmental Policy
- Initiatives to achieve
carbon neutrality - Climate-Related Disclosures
Based on TCFD Recommendations - CDP Score
Basic Environmental Policy
The Group is undertaking activities to contribute to the development of a sustainable society by striving for regional environmental conservation through proper responses to environmental risks under our Basic Environmental Policy and in compliance with laws and regulations.
- Contribute to the development of a sustainable society on a foundation of environmental management
- Establish and strive to continuously improve an environmental management system in addition to educating people and raising awareness of the environment
- Make efforts to reduce environmental impact in all aspects of manufacturing activities
- Develop and supply society with products that help reduce environmental impact
- Proactively promote environmental business that contributes to society
| Target | |
|---|---|
| Number of environmental incidents: | 0 |
Environmental Risk Management
The Group uses its ISO 14001 Management System to undertake proper responses to environmental risks in addition to continuously promoting environmental conservation activities. Regarding the air, water, land, waste disposal, and other relevant matters, we conduct environmental impact assessments tailored to the materials we handle, our facilities, and more, and undertake necessary and proper measures to reduce environmental impact.
Environmental education
We make efforts to enhance education and training to prevent accidents, for example by regularly providing our employees with education and practical training on environmental management. We aim to decrease the number of environmental incidents to zero through these initiatives.
Initiatives to achieve carbon neutrality
The Group recognizes global climate change as a major threat to the survival of humanity, and thus views bold efforts to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 to maintain a sustainable global environment and realize decarbonization as a key challenge of sustainability management.
To tackle this key challenge, in 2022, we formulated policy for achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, and are moving forward with business, and R&D to reduce CO2 emissions.
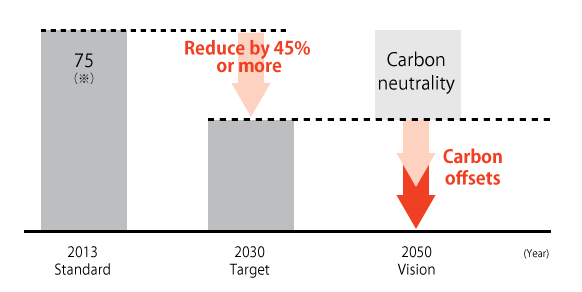
CO2 Emissions Reduction Scenario
The Group has up until now engaged in proactive energy-saving activities, transitioned to higher energy efficiency, and made other efforts to reduce CO2 emissions, and has launched initiatives to achieve the target of reducing emissions by 45% and more from 2015 levels by 2030 in an effort to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
-
в– Target for 2030
At Least 45% Reduction of CO2 Emissions from 2015 Levels
We aim to reduce CO2 emissions by at least 45% from 2015 levels by introducing in-house power generation utilizing renewable energy or the effects of energy-saving measures and efforts to improve energy efficiency.
-
в– Vision for 2050
Achieve Carbon Neutrality
We aim to tackle the challenge of developing and commercializing decarbonized production processes and flexibly utilize carbon offsets as we work to achieve carbon neutrality.
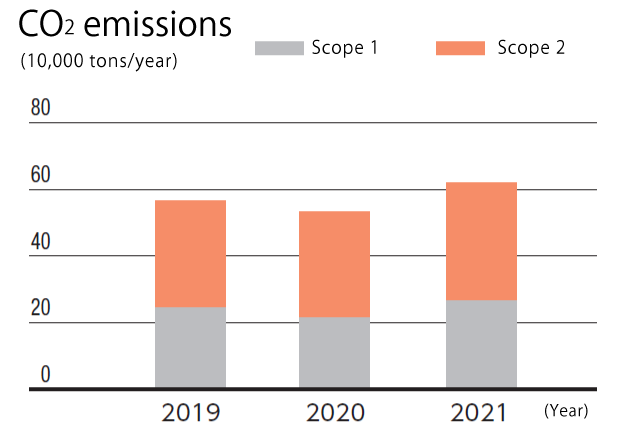
CO2 emissions of Nippon Denko Group (Scopes 1 and 2)
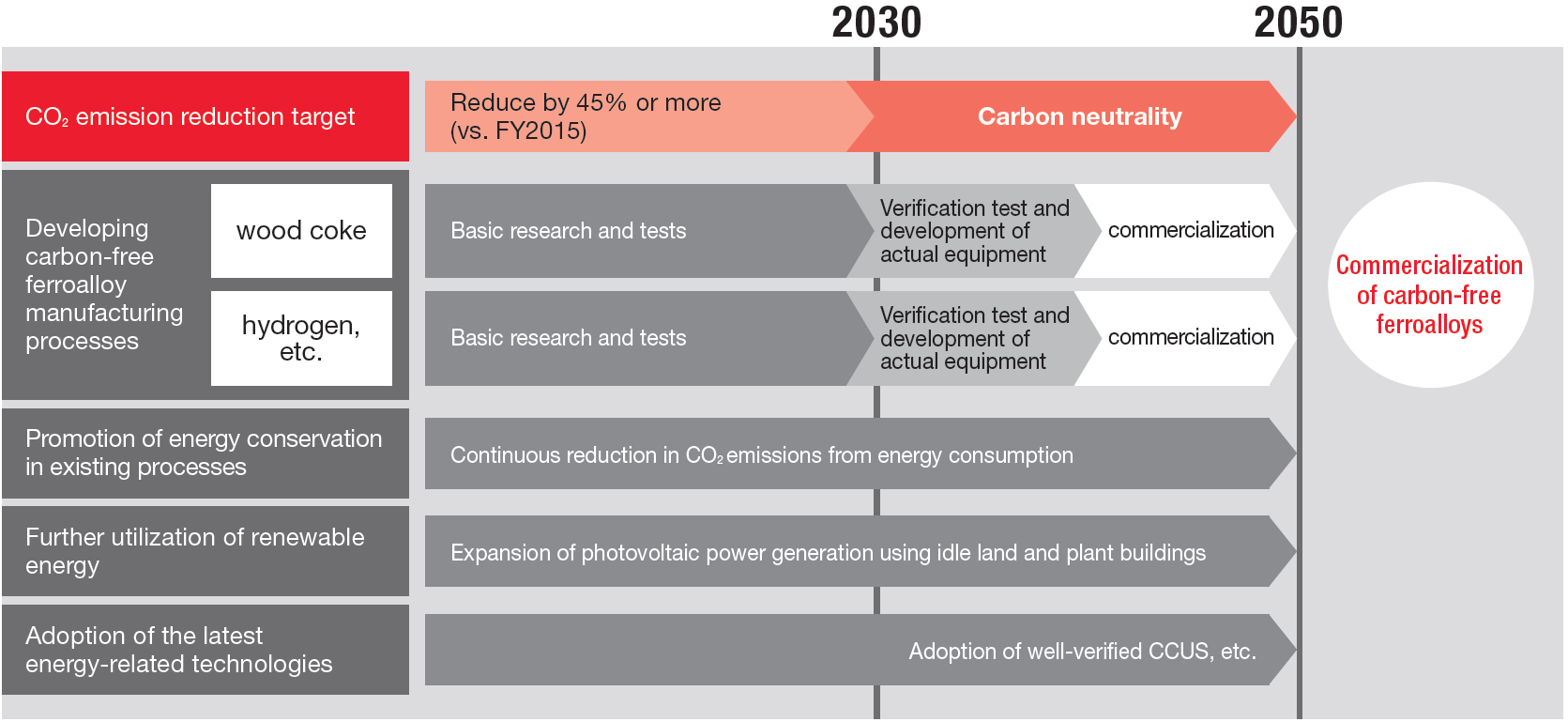
Roadmap toward Carbon Neutrality
Efforts to Reduce CO2 Emissions
The Group produces ferroalloys―namely ferromanganese, one of its main products―by using a reduction reaction that removes oxygen from naturally occurring manganese ore. This reduction reaction inevitably produces CO2 emissions because coal cokes is currently the optimal reduction agent for the process. The Group will continue transitioning to higher efficiency electricity and gas and converting to green energy in addition to tackling the challenge to develop and commercialize an innovative manufacturing process for reducing CO2 emissions in the process of manufacturing ferroalloys.

Initiatives
Research on innovative high-carbon ferromanganese reduction technology
We proposed “The Technology Development for Decarbonization and Energy Conservation in the Ferromanganese Production Process” for the Phase of Incubation Research and Development of the “Program to Develop and Promote the Commercialization of Energy Conservation Technologies to Realize a Decarbonized Society,” which is publicly solicited by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), and our proposal was adopted in June 2024. This proposal is based on the results obtained during the feasibility study research phase of the same program in 2023.
We will promote technological development towards the practical application of an innovative manufacturing process that will lead to reduced CO2 emissions and energy conservation in the reduction reaction process of ferroalloy production.
Utilization of renewable wood cokes
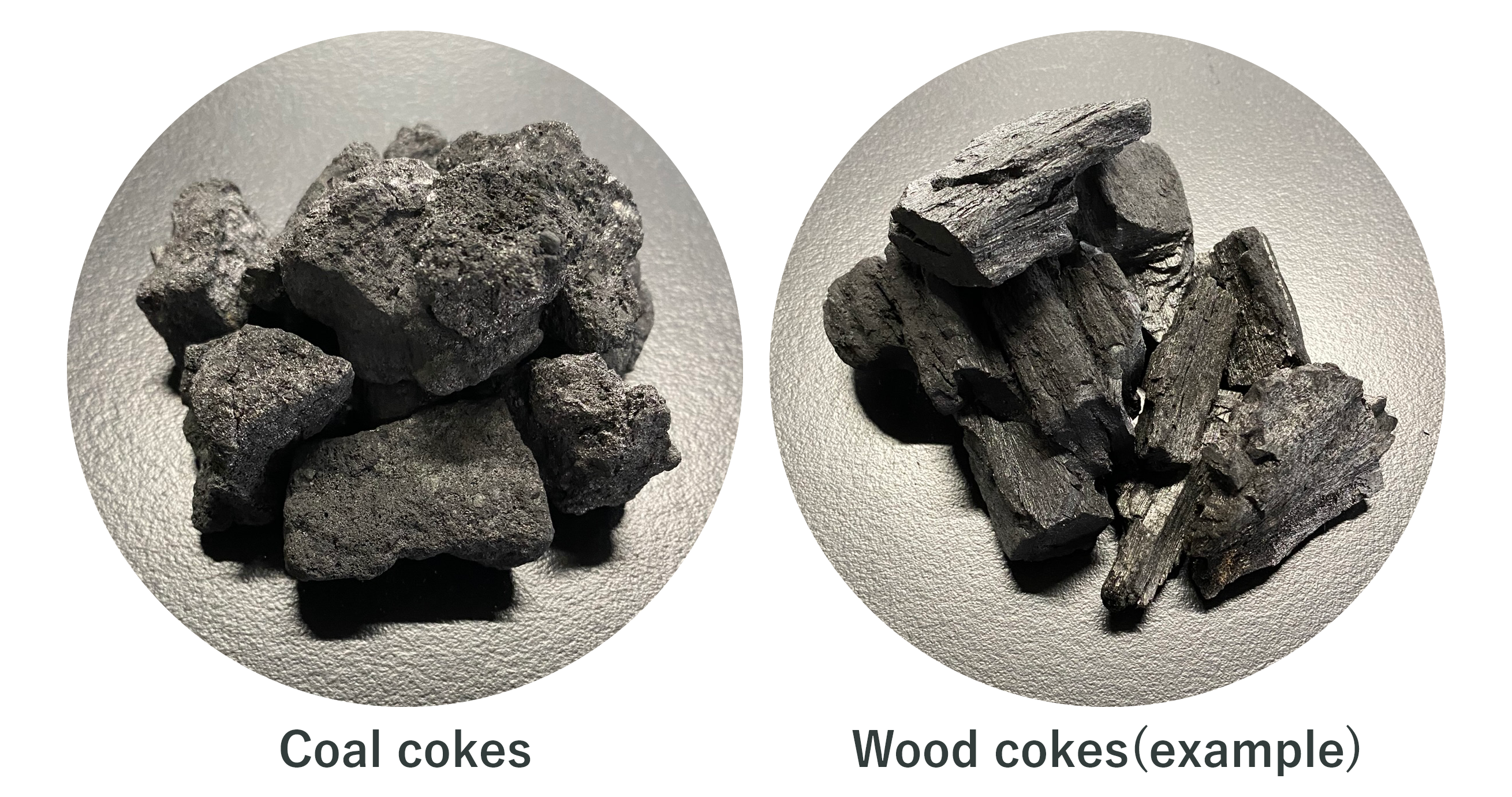

The use of coal cokes in the reduction of manganese ore generates CO2. Therefore, we are working to reduce CO2 emissions by using renewable wood cokes as a reducing agent instead of coal ones.
Our plan is to replace around 15% of coal cokes with wood cokes by 2030. To this end, we are currently promoting technological development for the use of wood cokes. This includes evaluating the quality and cost of wood cokes from multiple production areas, conducting basic research at the laboratory level in collaboration with external research institutions, and carrying out trials using actual electric furnaces at the Tokushima plant.
Promotion of energy conservation measures
We have been working to improve our energy consumption per unit of production, and we have been ranked in the highest S (excellent business operator) class for five consecutive years until 2024 in the business class evaluation system implemented by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy based on the Act on Rationalization of Energy Use and Shift to Non-fossil Energy. The class S is given to businesses that have achieved the target of reducing their average energy consumption per unit of production by 1% or more over a five-year period. We will continue to promote energy conservation measures, such as updating and renovating the equipment used in the current manufacturing processes in order to reduce energy consumption by 1% or more each year.
Participation in the Green Transformation (GX) League

We support the “GX League Basic Concept” proposed by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, and have been participating in the “GX League” since 2023. The GX League is a platform for companies taking on the challenge of GX. These companies aim to achieve carbon neutrality and social transformation by 2050, as well as sustainable growth in present and future societies. The GX League enables these companies to collaborate with other companies engaged in similar initiatives, including government and academic institutions. By participating in the GX League, we will accumulate knowledge and know-how on reducing CO2 emissions and promote sustainability-oriented management.
Climate-related disclosures based on TCFD recommendations
The Group recognizes global climate change as a major threat to the survival of humanity, and thus views bold efforts to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 to maintain a sustainable global environment and realize decarbonization as a key challenge of sustainability management. As part of this initiative, in February 2022, we announced our endorsement of the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and will disclose important information related to climate change in line with the TCFD framework as follows.
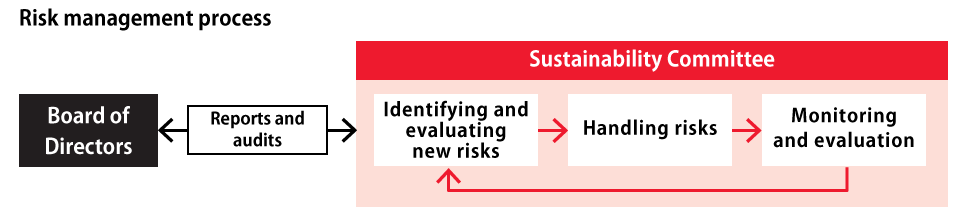
Governance
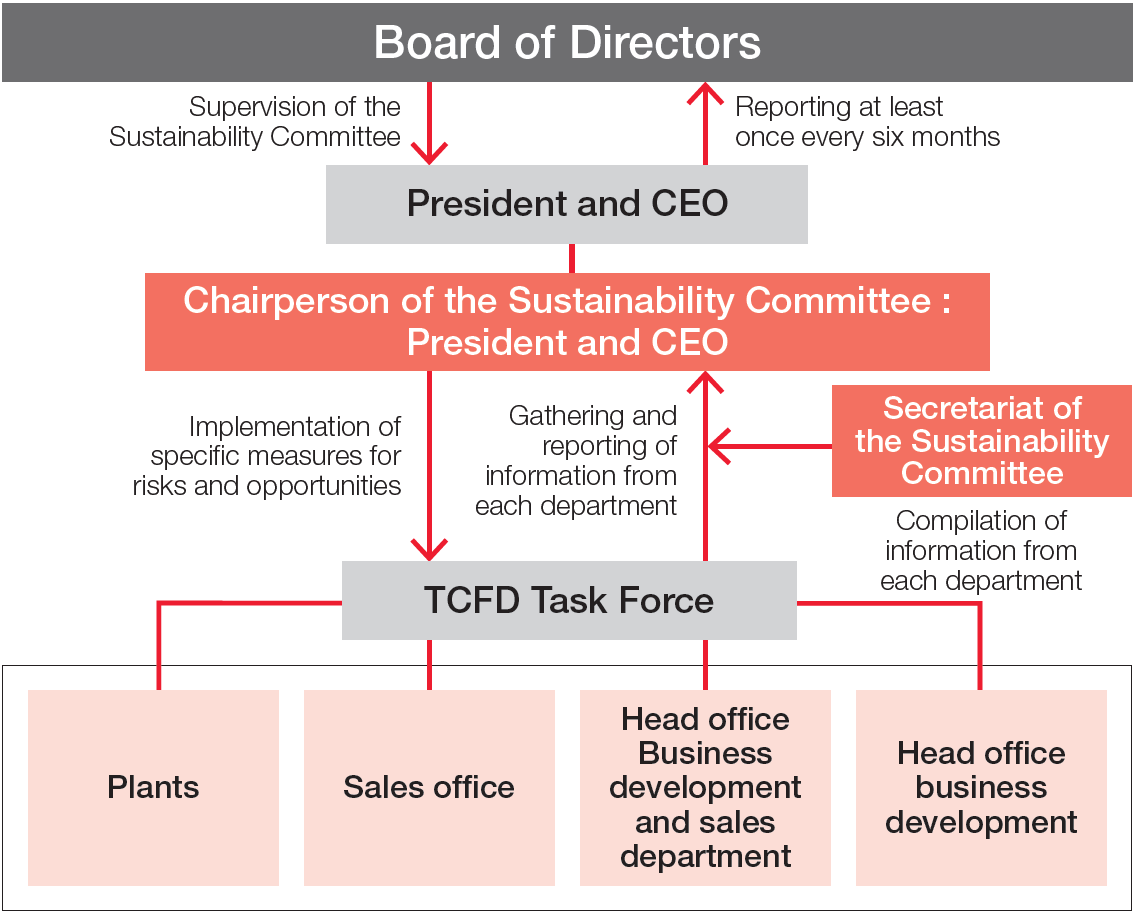
In January 2022, the Group established the Sustainability Committee as an organization directly under the Board of Directors to promote sustainability initiatives, including the response to climate change, and to further enhance corporate value in the medium/long term. This committee meets once a quarter and is chaired by President and CEO. The Sustainability Committee reviews companywide measures and monitors initiatives (reduction of GHG emissions as a KPI).
In addition, the committee chairperson will report on the matters discussed at the committee to the Board of Directors at least once every six months, and the Board of Directors makes recommendations to the Sustainability Committee on issues related to sustainability and climate change that have been discussed at the committee.
Structure for coping with climate change
Strategy
Analysis process
The Group believes that to realize sustainability management, it is important to analyze the impact of climate change on our business by classifying and risks and opportunities and ensure that our corporate management reflects appropriate responses. So, we have taken the following steps to review the risks and opportunities that climate change issues pose to our business. Specifically, using two climate change scenarios, the 1.5℃ to 2℃ scenario and the 4℃ scenario, we conducted analyses related to the transition in policies and market trends (transition risks/opportunities) as well as an analysis of physical changes due to disasters (physical risks/opportunities).

About climate change scenarios
1.5℃ to 2℃ scenario (decarbonization scenario)
This scenario aims to limit the rise of global average temperature to less than 1.5℃ to 2℃ compared to pre-industrial times, as efforts to achieve carbon neutrality become more active in order to mitigate the impact of climate change. In the 1.5℃ scenario, it is assumed that among the transition risks, the impact of policies and regulatory risks will be greater than in the 2℃ scenario.
4℃ scenario (high-emissions scenario)
This scenario assumes that no progress will be made in measures against climate change, and that the global average temperature will rise by approximately 4℃ by the end of this century compared to pre-industrial times. It is assumed that the impact of extreme weather events and the risk of rising sea levels will increase in terms of physical risk.
Assessment of Impacts of Risks and Opportunities and Selection of Countermeasures
Risk
In the below-2℃ scenario, there is a risk of increased costs due to the need to switch to renewable energy and low-carbon materials due to stricter regulations, while in the 4℃ scenario, there is a risk of increased costs due to intensifying natural disasters.
| Risk | Classification | Factors | Details of the Risk | Timeline | Impact Level | Countermeasure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition risk |
Policies/ Legal regulations |
Introduction of GHG emission regulations, carbon taxes, and the like |
Profitability compromised by the increased cost of fossil fuels and other elements of manufacturing | Medium term |
Large |
|
| Increase in the rate of renewable energy (change in power supply structure) |
Rise in electricity costs due to measures by electric power companies to increase the ratio of renewable energy | Medium term |
Large |
|
||
| Market | Increase in the cost of procuring manganese ore | Distribution costs increase as mining and transportation are decarbonized | Medium term |
Medium |
|
|
| Increase in the cost of procuring reducing agents | Increased costs associated with procurement of low-carbon reducing agents (wood cokes, etc.) | Medium term |
Medium |
|
||
| Physical risk |
Acute | Intensifying natural disasters (flooding and storm surges) | Deterioration in earnings due to suspension of business activities resulting from inundations at plants | Long term |
Medium |
|
| Intensifying natural disasters (typhoons) |
Deterioration in earnings due to suspension of business activities resulting from typhoon damage | Long term |
Medium |
Opportunity
Environmentally friendly businesses are expected to expand.
| Opportunity | Classification | Factors | Details of the Opportunity | Timeline | Impact Level | Countermeasure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opportunity | Products and services |
Consumer preference for low-CO2 products |
Growth of demand for green ferroalloys (Pertama Ferroalloys, an equity-method affiliate, manufactures ferroalloys [green ferroalloys] using hydroelectric power only) |
Medium term |
Medium |
|
| Evolution into a hydrogen based society |
Growth of demand for pure water production system used in hydrogen production | Medium/ long term |
Small |
|
||
| Market | Spread of EVs | Growth of demand for batteries and electronic components due to the spread of EVs (battery materials, boron oxide, zirconium oxide, ferroboron, etc.) | Medium term |
Medium |
|
- Scenarios used: [Transition risks] IEA WEO2023 NZE2050 / [Physical risks] IPCC RCP8.5 and IPCC AR6 SSP5-8.5
- Timeline: [Short term] within 1 year [Medium term] till 2030 [Long term] till 2050
- Impact level: [Large] Profit before income taxes of 1 billion yen or larger [Medium] Profit before income taxes of 100 million to less than 1 billion yen [Small] Profit before income taxes of less than 100 million yen
Risk Management
Process for identifying and assessing climate-related risks
After the TCFD identifies risks associated with climate change and we report them to the Sustainability Committee, the committee discusses the risks once a year. Risks that are deemed particularly important are reported to the Board of Directors once a year.
Process for controlling climate-related risks
The Sustainability Committee will monitor the identified climate change risks and deliberate countermeasures.
After reviewing the countermeasures, the Sustainability Committee will share them with relevant departments and take action to mitigate the risks.
Integration process for company-wide risk management
We have established an Internal Control Committee to manage non-climate-related company-wide risks identified by each department and group company in a unified manner. The Sustainability Committee reports transition risks, physical risks, and countermeasures to the Internal Control Committee, which then reports to the Board of Directors.
Metrics and Targets
The Group has announced a target to reduce CO2 emissions by at least 45% from 2015 levels by 2030 as described on p. 35. We will continue working to reduce CO2 emissions by introducing in-house power generation utilizing renewable energy, implementing energy-saving measures, and striving to improve energy efficiency. We will also start fundamental research on innovative decarbonized processes for manufacturing carbon-free ferroalloys, continue the transition to green-energy fuels, and make other efforts to proactively introduce the latest equipment and technology to dramatically improve productivity.
CDP Score: “B” rating for climate change in 2024
CDP is a UK charity-controlled non-governmental organization (NGO) that operates a global information disclosure system to help investors, companies, nations, regions, and cities manage their own environmental impact.




![close[]](/en/shared/img/sp/closeBtn.png)